

Imagine being able to understand the condition of your nerves every day, from the comfort of your own living room. Instead of waiting for routine appointments, individuals can now monitor their nerve health in real time, using specialized sensors designed to provide valuable insights into their nervous system. These technologies have emerged as reliable tools, harnessing the power of digital sensors and home electronics to bring nerve monitoring out of the clinic and directly into the homes of people across the United States.
Nerve health sensors work by detecting subtle physiological signals—such as skin temperature, sensitivity, vibration, and electrical responses—then translating this data into actionable information on mobile apps or connected devices. This means that early warning signs or changes in nerve function become far more accessible to track over time, giving users the chance to better understand how their nerves respond to everyday life or new therapies. For individuals with neuropathy or those at risk, these tools can make all the difference in maintaining proactive oversight of their own health journey.
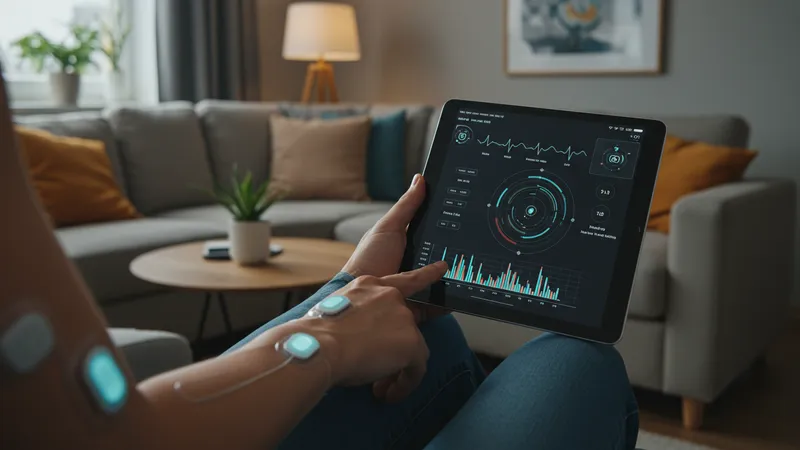

These nerve health devices emerged in response to a growing demand among Americans for accessible, noninvasive ways to track progression or changes in neuropathy. Historically, nerve diagnostics required clinical settings with specialized equipment, but now, everyday users in the United States benefit from having advanced sensor technology available at home.
The advantages of consistent nerve monitoring extend beyond simple awareness. By collecting objective data over time, users can detect patterns or subtle changes, sometimes catching potential concerns before symptoms become serious. Some American neurology practices even encourage patients with chronic nerve issues to use home sensors, as the longitudinal data supports more informed clinical decision-making.
These sensors differ from standard wearable health tech, such as heart rate trackers, because they’re designed to capture the intricate signals relevant to nerve function. They may use electrical, vibratory, or thermal measurement methods tailored specifically for detecting neuropathic changes, rather than general activity or wellness metrics.
What’s particularly striking is the way home-based nerve health sensors are changing how individuals engage with their healthcare providers. Many in the United States now share digital reports generated by these devices, creating a collaborative approach to managing neuropathy. As adoption continues to rise, understanding how to choose and use these sensors effectively is becoming an essential skill.
Page 1 has highlighted the key players and foundational insights into home-based nerve health monitoring. The deeper details reveal even more valuable insights ahead—especially about features, performance, user experience, and how these technologies are shaping neurology in the United States.
When examining the features that set home neuropathy sensors apart, accuracy and ease of use stand out as top priorities. Devices such as the Nervive Nerve Monitor are engineered with advanced electrodes and highly sensitive detection systems to capture nerve signals without requiring medical expertise. An intuitive interface guides users through each test, ensuring reliable results regardless of experience level. The sensors are designed to be comfortable for at-home use, emphasizing minimal invasiveness and simple daily routines.

Personalized data analytics is another significant feature provided by home sensors. NeuroPacer Sensor Kit users benefit from mobile dashboards that organize tracking over time, displaying clear visualizations of nerve conductivity and sensory data. These analytics enable the detection of trends and shifts unique to each user, which can be invaluable for ongoing management in the United States, where regular clinical visits may not always be possible.
Portability further enhances the appeal of these devices. The Checkpoint Home Neuropathy Sensor, for instance, fits neatly into a pocket or small case, enabling consistent monitoring whether at home or while traveling. This convenience has expanded usage beyond fixed home settings, matching the active lifestyles of many Americans seeking to seamlessly integrate health tracking into daily routines.
Reliable connectivity rounds out the most sought-after features. The latest models sync with smartphones and cloud services, allowing automatic report generation and secure data sharing with healthcare professionals. This feature streamlines communication and supports more informed therapy adjustments, a benefit especially valued in the diverse U.S. healthcare landscape.
Performance is a critical factor influencing trust in home-use neuropathy sensors. Clinical validation studies conducted in the United States have demonstrated that devices like the NeuroPacer Sensor Kit closely match the results of traditional in-clinic nerve conduction studies, often with less than five percent variance. The enhanced sensitivity of these tools allows for detection of subtle changes in nerve function—such as delayed sensory response—which could otherwise be missed in routine annual checkups.
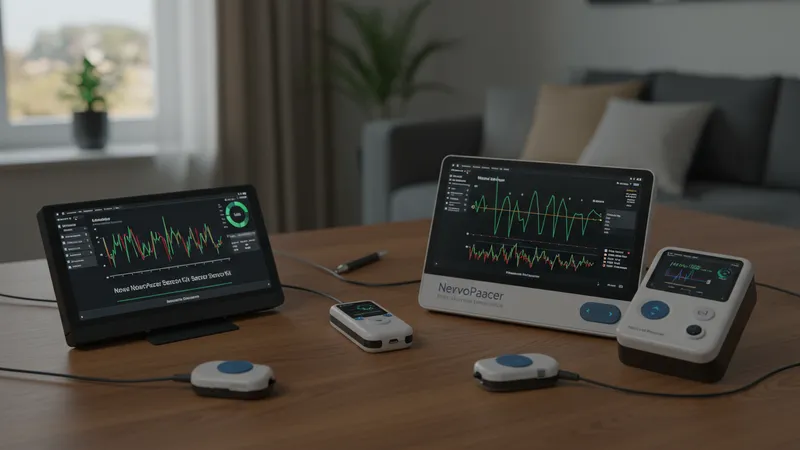

Repeatability is another pillar of performance. Top-tier home neuropathy sensors, such as the Nervive Nerve Monitor, achieve consistent measurements through built-in calibration routines. This ensures daily readings remain accurate over time, providing both users and clinicians with confidence in the data’s reliability. The result is a trusted longitudinal dataset that supports smarter, more personalized care strategies.
American users have also praised the increased granularity and frequency these sensors allow. While traditional diagnostics may involve a snapshot every few months, home-based tools can deliver daily, weekly, or monthly readings. This approach can capture fluctuations related to activity, sleep, or diet—offering a more holistic view of nerve health than isolated in-clinic measurements.
Wireless capabilities further boost usability and minimize sources of error. Devices like the Checkpoint Home Neuropathy Sensor utilize Bluetooth or Wi-Fi for seamless, low-latency communication with mobile devices, ensuring data is captured and transmitted promptly. Access to real-time updates can prompt timely action if nerve changes are detected, supporting a more proactive nerve health management strategy in the United States.
Consumers in the United States have shown growing enthusiasm for neuropathy sensors that fit easily into their daily routines. For instance, the setup process for the Nervive Nerve Monitor is designed to be swift—requiring just a few steps on a smartphone before users can begin a session. This plug-and-play design means even those without specialized knowledge find it approachable, removing a key barrier to widespread adoption.
Comfort during use is a high priority. With the NeuroPacer Sensor Kit, hypoallergenic adhesives and low-profile patches ensure the sensor remains almost unnoticeable throughout tests. This design enables repeated use throughout the week, a benefit particularly valued by those tracking changes or managing chronic neuropathy in busy American households.
Ongoing support and troubleshooting also contribute to positive experiences. Major brands provide digital user guides and direct contact with technical specialists, helping U.S. users quickly resolve issues that could disrupt data collection. Some offer integrated help features and FAQs within their apps to streamline self-service support.
Feedback from users frequently highlights the sensors’ ability to empower self-management. Instead of waiting for annual nerve assessments, Americans can proactively spot trends and share their information with healthcare professionals. This realignment of the traditional healthcare model demonstrates how technology is making meaningful self-tracking accessible to more people across the United States.
Neurologists across the United States are increasingly integrating home nerve sensor data into patient care. By reviewing time-stamped, longitudinal records collected from devices like the Checkpoint Home Neuropathy Sensor, clinicians can identify patterns and make more informed recommendations. This partnership enables a more connected patient-provider relationship, transforming episodic care into an ongoing dialogue grounded in real data.
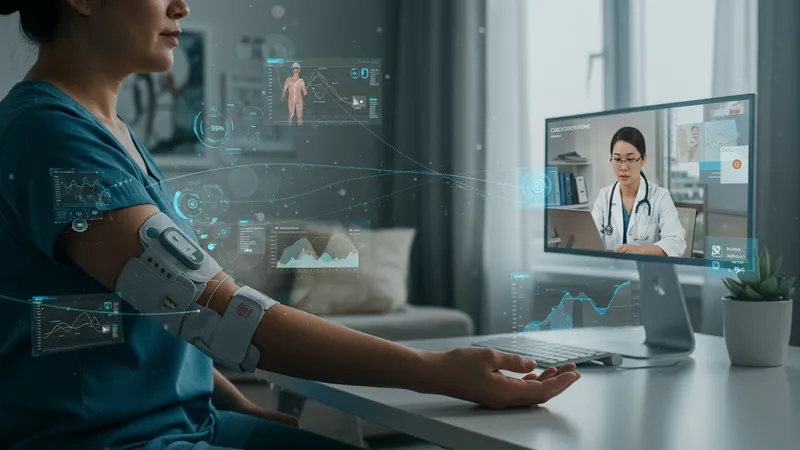

Insurance providers and healthcare systems in the U.S. have also begun to recognize the benefits of remote nerve health monitoring. Some are exploring reimbursement options for sensor devices, acknowledging how proactive data tracking can support earlier interventions and contribute to better outcomes for neuropathy patients. This development hints at a future in which home-based monitoring is a standard part of nerve care workflows.
Home-use neuropathy sensors can also support participation in clinical studies and trials within the United States. Researchers now have the capability to recruit participants nationwide and gather high-fidelity nerve data remotely. This advancement accelerates research while minimizing geographic barriers traditionally associated with clinic visits, further advancing the field of neuropathy research.
As these technologies continue to develop, their potential for contributing to public health data and population-level insights becomes more apparent. U.S. health authorities could eventually leverage anonymized sensor data to identify trends in nerve health across regions, ages, or risk groups, supporting larger public health strategies focused on neurological well-being.